Translator’s note: This is the 16th article of the series “Cloud Foundry 100-day Challenge selection”. “#068” in the title means that it is 68th (published on September 29, 2015) in the original Japanese series.
Original Author: Takeshi MORIKAWA (GitHub) (company)
The 68th topic of “Cloud Foundry 100-Day Challenge” is spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo. This is an application that works as a Cloud Foundry (“CF”) service broker, in a category similar to postgresql-cf-service-broker from Article #002. By deploying it, the application allows us to easily use MongoDB as a service.
Basic Information
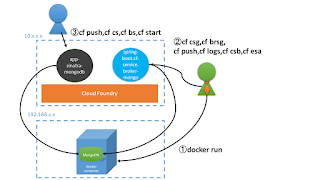
The overall process can be summarized in the below image:
The procedure can be summarized as follows:
- Preparing MongoDB (ver. 2.6) instance
- Deploying spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo
- Making application usable as service broker
Preparing MongoDB (ver. 2.6) Instance
Since this is for a experimental purpose, we decided to prepare MongoDB (ver 2.6) with Docker.
The summary of this section is as follows:
- 1) Installing Docker
- 2) Installing MongoDB Client
- 3) Running MongoDB Docker Image
Installing Docker
CF runs on Ubuntu, so we will also run the MongoDB Docker image on Ubuntu. First, we install Docker on Ubuntu.
$ sudo apt-get install -y docker.io
Verification:
$ sudo docker version
Client:
Version: 1.8.2
API version: 1.20
Go version: go1.4.2
Git commit: 0a8c2e3
Built: Thu Sep 10 19:19:00 UTC 2015
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Server:
Version: 1.8.2
API version: 1.20
Go version: go1.4.2
Git commit: 0a8c2e3
Built: Thu Sep 10 19:19:00 UTC 2015
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Installing MongoDB Client
NOTE: The purpose of this process is to enable checking MongoDB. It is not essential for running spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo, so it can be omitted.
$ sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-clients
Verification:
$ mongo --version
MongoDB shell version: 2.4.9
Running MongoDB Docker Image
Retrieving Docker Image
$ sudo docker pull mongo:2.6
NOTE: The version of MongoDB is specified by the tag 2.6 because spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo will not work properly unless the version of MongoDB is 2.6.
Starting Docker Image
While setting the host’s port 27017 to transfer to the container’s port 27017, start the obtained Docker image.
$ sudo docker run -p 27017:27017 -d mongo:2.6
Checking Connectivity
$ mongo --port 27017
MongoDB shell version: 2.4.9
connecting to: 127.0.0.1:27017/test
This completes the preparation of the MongoDB instance.
Deploying spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo
Next, we deploy spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo on CF.
This is the summary of procedures:
- 0) Preparing for Deployment
- 0.1) Installing JDK and Gradle
- 0.2) Retrieving Source Code
- 0.3) Modifying Source Code
- 0.4) Building Application
- 0.5) Creating Org and Space
- 0.6) Configuring Application Security Group
- 1) Deployment
- 1.1) Pushing Application
Preparing for Deployment
Installing JDK and Gradle
As the name suggests, this is a spring-boot application, so we install JDK and Gradle.
Oracle JDK 8
We retrieve a tarball that is proper for our environment from the page of Oracle JDK 8.
NOTE: At the time of the article, the latest version is jdk-8u60-linux-x64.tar.gz.
$ ls -lha jdk-8u60-linux-x64.tar.gz
-rw-rw-r-- 1 morika-t morika-t 173M Aug 7 08:32 jdk-8u60-linux-x64.tar.gz
Expand the tarball:
$ tar zxfv jdk-8u60-linux-x64.tar.gz
Configure JAVA_HOME and PATH.
$ export JAVA_HOME=~/work/jdk1.8.0_60
$ export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
Check the version:
$ java -version
java version "1.8.0_60"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_60-b27)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.60-b23, mixed mode)
Gradle
$ wget https://services.gradle.org/distributions/gradle-2.5-all.zip
$ unzip gradle-2.5-all.zip
Configure GRADLE_HOME and PATH.
$ export GRADLE_HOME=~/work/gradle-2.5
$ export PATH=$GRADLE_HOME/bin:$PATH
Check the version:
$ gradle -version
------------------------------------------------------------
Gradle 2.5
------------------------------------------------------------
Build time: 2015-07-08 07:38:37 UTC
Build number: none
Revision: 093765bccd3ee722ed5310583e5ed140688a8c2b
Groovy: 2.3.10
Ant: Apache Ant(TM) version 1.9.3 compiled on December 23 2013
JVM: 1.8.0_60 (Oracle Corporation 25.60-b23)
OS: Linux 3.13.0-55-generic amd64
Retrieving Source Code
Clone the source code of the application from GitHub.
$ git clone https://github.com/spgreenberg/spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo
$ cd spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo
Modifying Source Code
Before building the application, we will modify the source code to adjust the application to Service Broker API version 2.5 which is supported by cf-release v211, the environment used in this post.
NOTE: Version 2.4 of Service Broker API is the version that corresponds to the latest code for spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo at the time of this article.
Modification to Not Verify Header for Service Broker API Version
$ vi src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/community/servicebroker/mongodb/config/CatalogConfig.java
$ git diff src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/community/servicebroker/mongodb/config/CatalogConfig.java
diff --git a/src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/community/servicebroker/mongodb/config/CatalogConfig.java b/src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry
index 295b844..9b51e87 100644
--- a/src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/community/servicebroker/mongodb/config/CatalogConfig.java
+++ b/src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/community/servicebroker/mongodb/config/CatalogConfig.java
@@ -8,6 +8,7 @@ import java.util.Map;
import org.cloudfoundry.community.servicebroker.model.Catalog;
import org.cloudfoundry.community.servicebroker.model.Plan;
import org.cloudfoundry.community.servicebroker.model.ServiceDefinition;
+import org.cloudfoundry.community.servicebroker.model.BrokerApiVersion;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@@ -15,6 +16,11 @@ import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
public class CatalogConfig {
@Bean
+ public BrokerApiVersion brokerApiVersion() {
+ return new BrokerApiVersion();
+ }
+
+ @Bean
Modification to Add requires: syslog_drain in Service Catalog
Reference URL:
http://cf-dev.70369.x6.nabble.com/cf-dev-Document-for-service-broker-api-version-2-5-tp537p582.html
http://docs.cloudfoundry.org/services/app-log-streaming.html
$ vi src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/community/servicebroker/mongodb/config/CatalogConfig.java
$ git diff src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/community/servicebroker/mongodb/config/CatalogConfig.java
@@ -30,7 +36,7 @@ public class CatalogConfig {
getPlanMetadata())),
Arrays.asList("mongodb", "document"),
getServiceDefinitionMetadata(),
- null,
+ Arrays.asList("syslog_drain"),
null)));
}
Configuring MongoDB Connection
$ vi src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/community/servicebroker/mongodb/config/MongoConfig.java
$ git diff src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/community/servicebroker/mongodb/config/MongoConfig.java
diff --git a/src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/community/servicebroker/mongodb/config/MongoConfig.java b/src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/c
index 4f403c0..d12c07a 100644
--- a/src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/community/servicebroker/mongodb/config/MongoConfig.java
+++ b/src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/community/servicebroker/mongodb/config/MongoConfig.java
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ public class MongoConfig {
@Bean
public MongoClient mongoClient() throws UnknownHostException {
- return new MongoClient();
+ return new MongoClient("192.168.15.91", 27017);
}
}
Building Application
$ ./gradlew build -x test
Creating Org and Space
Like postgresql-cf-service-broker from Article #002 , we create a specific org and space for deploying the service broker.
We took and used one created in the previous article; when creating from scratch, the following commands need to be run:
$ cf create-org admin
$ cf create-space svcs
Configuring Application Security Group
The environment for this post is built with bosh-lite, whose default settings do not allow applications to connect to private addresses (10.*.*.*, 192.168.*.*). The MongoDB we built this time exists on 192.168.*.*, so we configure a security group for it.
Creating Security Group
We create an application security group that allows access to the MongoDB instance built previously.
First, we create a file with rules (in JSON format).
$ vi ~/spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo.security-groups.json
$ cat ~/spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo.security-groups.json
[
{
"protocol": "tcp",
"destination": "192.168.15.91",
"ports": "27017"
}
]
Registering Security Group
$ cf create-security-group spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo-security-groups ~/spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo.security-groups.json
Verification:
$ cf security-group spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo-security-groups
Getting info for security group spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo-security-groups as admin
OK
Name spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo-security-groups
Rules
[
{
"destination": "192.168.15.91",
"ports": "27017",
"protocol": "tcp"
}
]
No spaces assigned
Binding to Default Running Security Group
By configuring these settings, all applications on the same CF will be able to access the MongoDB instance when run.
$ cf bind-running-security-group spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo-security-groups
Deployment
Pushing Application
We just cf push, as manifest.yml is already prepared.
$ cf push
App started
OK
App mongo-broker was started using this command `SERVER_PORT=$PORT $PWD/.java-buildpack/open_jdk_jre/bin/java -cp $PWD/.:$PWD/.java-bu
ildpack/spring_auto_reconfiguration/spring_auto_reconfiguration-1.10.0_RELEASE.jar -Djava.io.tmpdir=$TMPDIR -XX:OnOutOfMemoryError=$PW
D/.java-buildpack/open_jdk_jre/bin/killjava.sh -Xmx382293K -Xms382293K -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=64M -XX:MetaspaceSize=64M -Xss995K org.spr
ingframework.boot.loader.WarLauncher`
Showing health and status for app mongo-broker in org admin / space svcs as admin...
OK
requested state: started
instances: 1/1
usage: 512M x 1 instances
urls: mongo-broker.10.244.0.34.xip.io
last uploaded: Thu Sep 24 09:25:12 UTC 2015
stack: cflinuxfs2
buildpack: java-buildpack=v3.0-https://github.com/cloudfoundry/java-buildpack.git#3bd15e1 java-main open-jdk-jre=1.8.0_60 spring-auto-
reconfiguration=1.10.0_RELEASE
state since cpu memory disk details
#0 running 2015-09-24 06:25:57 PM 11.9% 329.8M of 512M 0 of 1G
Making Aplication Usable as Service Broker
We let the CF environment recognize the application as a service broker. The summary of procedures in this section are as follows:
- 1) Checking Credentials for Service Broker Registration
- 2) Registering as Service Broker
- 3) Checking Label Information to Enable Access on Marketplace
- 4) Enabling Access on Marketplace
Checking Credentials for Service Broker Registration
We check the log using the --recent option of cf logs.
$ cf logs mongo-broker --recent
The section after password: in the following log is the password used for Service Broker registeration.
The user name is fixed as user.
2015-09-25T10:32:39.97+0900 [App/0] OUT 2015-09-25 01:32:39.972 INFO 29 --- [ main] b.a.s.AuthenticationManagerConfiguration :
2015-09-25T10:32:39.97+0900 [App/0] OUT Using default security password: cbbed27c-b42a-489b-8d1b-ce3cb9c6e779
2015-09-25T10:32:40.24+0900 [App/0] OUT 2015-09-25 01:32:40.245 INFO 29 --- [ main] s.b.c.e.t.TomcatEmbeddedServletCon
tainer : Tomcat started on port(s): 61139/http
2015-09-25T10:32:40.24+0900 [App/0] OUT 2015-09-25 01:32:40.248 INFO 29 --- [ main] o.c.c.s.mongodb.config.Application
: Started Application in 7.613 seconds (JVM running for 8.284)
Registering as Service Broker
$ cf create-service-broker mongodb user cbbed27c-b42a-489b-8d1b-ce3cb9c6e779 http://mongo-broker.10.244.0.34.xip.io
Checking Label Information to Enable Access on Marketplace
The label name for registration is “Mongo DB”. To check the value, we look at the value of the second argument of ServiceDefinition of CatalogConfig.java.
$ vi src/main/java/org/cloudfoundry/community/servicebroker/mongodb/config/CatalogConfig.java
23 @Bean
24 public Catalog catalog() {
25 return new Catalog( Arrays.asList(
26 new ServiceDefinition(
27 "mongo",
28 "Mongo DB",
29 "A simple mongo implementation",
30 true,
31 false,
Enabling Access on Marketplace
By completing this procedure, we provide the service plan to all users.
$ cf enable-service-access "Mongo DB"
Verification:
$ cf service-access
broker: mongodb
service plan access orgs
Mongo DB Default Mongo Plan all
$ cf marketplace
service plans description
Mongo DB Default Mongo Plan* A simple mongo implementation
Checking Service Broker Behavior using Sample Application
Creating Service
$ cf create-service 'Mongo DB' 'Default Mongo Plan' mongodb-test
Cloning Sample Application
We clone a simple Sinatra application that uses MongoDB.
https://github.com/nota-ja/app-sinatra-mongodb.git
$ git clone https://github.com/nota-ja/app-sinatra-mongodb.git
$ cd app-sinatra-mongodb
Pushing Sample Application
$ cf push sinatra-mongo --no-start
Binding Service
$ cf bind-service sinatra-mongo mongodb-test
Starting Sample Application
$ cf start sinatra-mongo
Reading from / Writing to MongoDB
Here, let’s store the data “Taro” to the key “1”.
$ curl -X POST http://sinatra-mongo.10.244.0.34.xip.io/service/mongo/1 -d 'Taro'
We get an output that confirms “Taro”.
Taro
Then read the data for key name “1”.
$ curl http://sinatra-mongo.10.244.0.34.xip.io/service/mongo/1
We get back the stored “Taro”.
Taro
Let’s restart the application.
$ cf restart sinatra-mongo
And read the data for key name “1” again.
$ curl http://sinatra-mongo.10.244.0.34.xip.io/service/mongo/1
The data is persistent even after a restart, so we still get back the stored data “Taro”.
Taro
Software Used in This Post
- cf-release (v211)
https://github.com/cloudfoundry/cf-release/tree/v211
( https://github.com/cloudfoundry/cf-release/tree/2121dc6405e0f036efa4dba963f7f49b07e76ffa ) - bosh-lite
https://github.com/cloudfoundry/bosh-lite/tree/552dc6869600c5350eb7ffb4fb9c9c5e79e3889d - CF CLI (v6.12.0-8c65bbd-2015-06-30T00:10:31+00:00)
https://github.com/cloudfoundry/cli/releases/tag/v6.12.0 - spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo
https://github.com/spgreenberg/spring-boot-cf-service-broker-mongo/tree/c906301ecad09e76118bb3186a3ad2dd84bb642d - Docker Image
REPOSITORY=mongo, TAG=2.6



![Stark & Wayne’s Dr. Nic on Winning in Production [Video]](https://www.cloudfoundry.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/cloud-foundry-blog-image-300x167.gif)
![Cloud Development Best Practices – Common Anti-Patterns in Building Scalable Microservices with Cloud Foundry [Reblog]](https://www.cloudfoundry.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/blogimage-reblog-scaling-300x127.jpg)